Analyze Lisa’s Dream Again From an Information Processing Perspective.
Information security in the broadest sense is a combination of ways to protect data from accidental or deliberate exposure. The owner of the data bears losses regardless of whether the impact was caused by natural or artificial factors.
Principles of information security
Integrity means the adequacy of data to proceed the original form and structure during storing and after repeated transfers. Only the possessor or user with legal access to the data has the right to edit, delete or supplement the data.
Confidentiality reveals the need to restrict admission to data resources for a certain circle of people. During actions and operations, information is merely accessible to users who are included in the information systems and have been successfully authenticated.
Accessibility means that public information should exist made available to authorized users of resources in a timely and unhindered mode.
Authenticity shows that the information belongs to a trusted person or possessor who at the aforementioned fourth dimension acts as a source of data.
Provision and sustainment of information security involves a set of various measures to prevent, monitor and eliminate unauthorized third-party access. Information security measures are also aimed at protection from dissentious, distorting, blocking or copying information. All tasks should be addressed simultaneously, only and then complete and reliable protection is ensured.
Keep corporate information safe with a gratis trial!
Principal questions about the data protection method are particularly astute when hacking or theft with distortion of information pb to severe consequences or financial damages.
At that place is the post-obit logical concatenation of information transformation created with modeling:
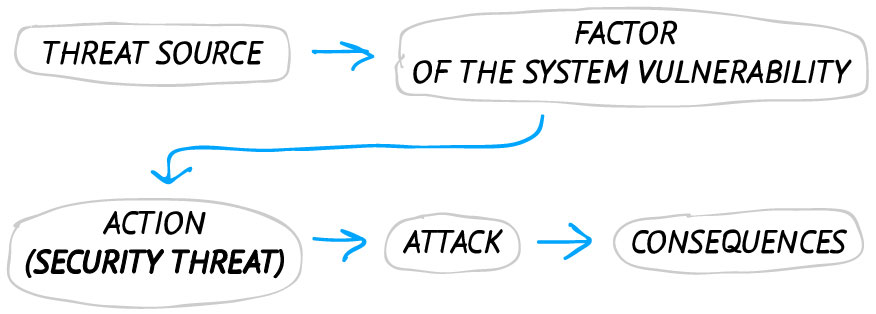
Types of information security threats
Data threat is a potentially possible influence or impact on an automated organisation with the subsequent damage to someone's needs.
To date, there exist more than ane hundred positions and types of threats to the information arrangement. It is extremely important to clarify all risks using different diagnostic techniques. Based on the analyzed detailed indicators, you can competently build a arrangement of protection against threats in the information space.
Classification of security vulnerabilities
Information security threats are non manifested independently but through possible contact with the gaps in the protection system, or factors of vulnerability. The threat leads to the disruption in systems on a specific carrier.
The main vulnerabilities are caused by the following factors:
- Shortcomings of software or hardware
- Different characteristics of the structure of automated systems in the information flow
- Some operational processes of the system are inadequate
- Inaccuracy of information commutation protocols and interface
- Difficult operating conditions and conditions in which the information is located.
Most oftentimes the sources of threats are triggered in gild to obtain illegal benefits after dissentious information. However, accidental consequence of threats due to insufficient protection and mass assail of a threatening cistron is also possible.
Vulnerabilities tin can be:
- Objective
- Random
- Subjective.
If you eliminate or at least mitigate the impact from vulnerabilities, you tin can avoid a significant threat meant to damage the storage system.
Random vulnerabilities
These factors vary depending on unforeseen circumstances and features of the information environment. They are almost impossible to predict in the information space, but you have to be prepared to apace eliminate them. Applied science and technical investigation or a response attack will help to mitigate the following problems:
1. Organization failures:
- Caused by malfunctions of technical ways at different levels of processing and storage of information (including those responsible for organisation performance and access to information technology).
- Malfunctions and obsolete elements (demagnetization of data carriers, such as diskettes, cables, connection lines and microchips).
- Malfunctions of different software that supports all links in the chain of data storage and processing (antiviruses, awarding and service programs).
- Malfunctions of auxiliary equipment of information systems (power manual failures).
ii. Factors weakening data security:
- Damage to communications such as water supply, electricity, ventilation and sewerage.
- Malfunctions of enclosing devices (fences, walls in buildings, housing of the equipment where information is stored).
Objective vulnerabilities
They depend on the technical design of the equipment which is installed on the object requiring protection, every bit well as its characteristics. It is impossible to escape all these factors, but their partial elimination can exist accomplished through technology techniques in the post-obit cases:
ane. Related to emission technical means:
- Electromagnetic techniques (side emission and signals from cablevision lines, elements of technical means).
- Audio versions (acoustic or with vibration signals).
- Electrical (sideslip of signals into the circuits of electrical network, through the consecration into the lines and conductors, because of uneven current distribution).
2. Activated:
- Malware, illegal programs, technological exits from programs which are together called 'implant tools'.
- Hardware implants: introduced directly into phone lines, electrical networks or premises.
three. Due to the characteristics of a protected object:
- Object location (visibility and absence of a controlled zone around the information object, presence of vibration or sound reflecting elements around the object, presence of remote elements of the object).
- Organization of data exchange channels (apply of radio channels, charter of frequencies or utilise of shared networks).
four. Those that depend on the characteristics of carriers:
- Parts with electro-acoustic modifications (transformers, telephone devices, microphones and loudspeakers, inductors).
- Elements under the influence of electromagnetic field (carriers, microcircuits and other elements).
Subjective vulnerabilities
In most cases, the vulnerabilities of this subtype issue from inadequate employee actions at the level of storage and protection system development. Eliminating such factors is possible using hardware and software:
1. Inaccuracies and gross errors that violate information security:
- At the stage of loading the set software or preliminary algorithm evolution, every bit well as during its utilize (perchance, during daily use or during information entry).
- When managing programs and data systems (difficulties in the preparation to work with the arrangement, individual set upwards of services, manipulation of data flows).
- During the use of technical equipment (during switch-on or switch-off, the use of devices for transmitting or receiving information).
2. Organisation malfunctions in the information surround:
- The mode of protection of personal data (the problem may be acquired by laid-off employees or current employees during off-hours when they get unauthorized admission to the arrangement).
- Safety and security mode (when accessing facilities or technical devices).
- While working with devices (inefficient free energy use or improper equipment maintenance).
- While working with information (change of information, its saving, search and devastation of data, elimination of defects and inaccuracies).
Vulnerability ranking
Specialists should consider and evaluate each vulnerability. Therefore, it is important to determine the criteria for assessing the threat of impairment to the protection and the probability of its breakage or bypassing. The indicators are calculated with the use of ranking. There are three main criteria:
- Accessibility is a benchmark that takes into account how convenient it is for a threat source to apply a particular blazon of vulnerability to disrupt information security. The indicator includes the technical information of the information carrier (such every bit equipment dimensions, its complication and cost, too as the possibility of using non-specialized systems and devices for hacking information systems).
- Fatality is a characteristic that assesses the vulnerability impact on the ability of programmers to cope with the consequences of the threat for information systems. When assessing merely objective vulnerabilities, it is necessary to define their information capacity or the ability to transmit to another place a useful indicate with confidential information without deforming it.
- Quantity is a characteristic of counting the parts of information storage and implementation systems which are prone to whatever vulnerability.
To find out the accurate information about protection level, yous need to engage the analytical department. They volition evaluate all the vulnerabilities and will make an information map with five point grading calibration. The one corresponds to the minimal impact on the protection and its bypassing while the 5 corresponds to the maximum impact and, accordingly, the danger. The results are recorded in one tabular array, and the impact level is broken downwardly into categories for convenient calculation of the vulnerability factor.
What sources threaten data security?
Threats bypassing the protection of information security can be divided into several categories. The concept of categories is mandatory, since information technology simplifies and systematizes all factors without exception. The chief parameters are
1. The degree of intentionality of intervention in the data protection system:
- Threats caused by unwitting employees in the information dimension
- Threats triggered past fraudsters for personal proceeds.
two. Signs of occurrence:
- Artificial information security threat provoked by human hands
- Natural threatening factors beyond the control of data protection systems caused by natural disasters.
iii. Classification of the firsthand cause of the threat. The perpetrator can exist:
- A person who disclose confidential information by bribing visitor employees.
- A natural gene like a ending or local disaster.
- Software with the utilise of specialized devices or the introduction of malicious code in technical means which disturbs the performance of the organisation.
- Accidental deletion of data, authorized software and hardware funds, failure of the operating system.
4. Severity of threats on information resources:
- At the moment of information processing in the information space (mailings from virus utilities).
- At the time of receiving new information.
- Regardless of the operation of information storage system (in the case of breaking ciphers or cryptographic protection of information).
Notice INTERNAL SECURITY THREATS
In that location is another classification of IS threats. Information technology is based on other parameters and is also used during the assay of the system malfunction or hacking. The following is taken into business relationship:
Threat source condition:
- In the arrangement itself, which leads to operational errors and failures when using Equally resources.
- Within the As'due south visibility, for example, the use of listening equipment, the theft of information in the printed form or the theft of records from data carriers.
- Fraud outside the coverage surface area of the AS. The information can be captured during the transfer through communication paths, incidental capture from audio-visual or electromagnetic emission of devices.
Impact degree:
- An agile security threat that changes the structure and nature of the arrangement, for case, the use of malicious viruses or Trojans.
- Passive threat steals information through copying, sometimes existence hidden. Information technology does not make changes to the data system.
Amercement
Severity and manifestations of a impairment can be different:
- Non-pecuniary and pecuniary amercement caused to individuals whose information was stolen.
- Financial loss with regard to the expenses incurred on restoring information systems.
- Material costs associated with the inability to perform piece of work because the information security system was changed.
- Reputational harm associated with the brand reputation and resulting in disturbed relations at global level.
The person who committed the offense (received unauthorized admission to information, or hacked into the protection organization) can cause damage. Damage can also occur regardless of the subject owning information, simply considering of external factors and impacts (technological and natural disasters). In the first case, the responsibility falls on the field of study, the components of the crime are divers, and offenders are punished through judicial proceedings. An act can be committed:
- With a criminal intent (direct or indirect)
- Through negligence (without intentional damage).
The punishment for an offense is chosen according to the electric current national legislation or according to the criminal code in the first example. If the crime is committed through negligence, and the damage incurred is small, the case will exist under civil, administrative or mediation police.
Sign up for a free trial
johnsonlowent1951.blogspot.com
Source: https://searchinform.com/infosec-blog/2019/08/17/fundamentals-of-is-data-protection/information-security-threats/

0 Response to "Analyze Lisa’s Dream Again From an Information Processing Perspective."
Post a Comment